What does citric acid cycle mean?
Definitions for citric acid cycle
cit·ric acid cy·cle
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word citric acid cycle.
Princeton's WordNet
Krebs cycle, Krebs citric acid cycle, citric acid cycle, tricarboxylic acid cyclenoun
in all plants and animals: a series of enzymatic reactions in mitochondria involving oxidative metabolism of acetyl compounds to produce high-energy phosphate compounds that are the source of cellular energy
Wiktionary
citric acid cyclenoun
An alternative name for the Krebs cycle.
Wikipedia
Citric acid cycle
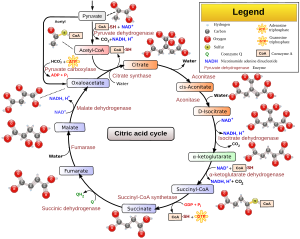
The citric acid cycle (CAC) – also known as the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and carbon dioxide. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically. Even though it is branded as a 'cycle', it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from the citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid, often called citrate, as the ionized form predominates at biological pH) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. The cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the citric acid cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP. In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, which lack mitochondria, the citric acid cycle reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. The overall yield of energy-containing compounds from the TCA cycle is three NADH, one FADH2, and one GTP.
ChatGPT
citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and carbon dioxide. It also provides precursors for many compounds including some amino acids and is therefore an essential part of the metabolic pathway in cells.
Wikidata
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle — also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle, or the Krebs cycle. — is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide. In addition, the cycle provides precursors including certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically. The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid that is first consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable energy in the form of ATP. In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. Bacteria also use the TCA cycle to generate energy, but since they lack mitochondria, the reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the plasma membrane rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
U.S. National Library of Medicine
Citric Acid Cycle
A series of oxidative reactions in the breakdown of acetyl units derived from GLUCOSE; FATTY ACIDS; or AMINO ACIDS by means of tricarboxylic acid intermediates. The end products are CARBON DIOXIDE, water, and energy in the form of phosphate bonds.
Matched Categories
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of citric acid cycle in Chaldean Numerology is: 2
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of citric acid cycle in Pythagorean Numerology is: 1
Translations for citric acid cycle
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
Get even more translations for citric acid cycle »
Translation
Find a translation for the citric acid cycle definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"citric acid cycle." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2025. Web. 6 Mar. 2025. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/citric+acid+cycle>.






Discuss these citric acid cycle definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In