What does MESON mean?
Definitions for MESON
ˈmɛz ɒn, ˈmɛs-, ˈmeɪ zɒn, -sɒnme·son
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word MESON.
Princeton's WordNet
meson, mesotronnoun
an elementary particle responsible for the forces in the atomic nucleus; a hadron with a baryon number of 0
GCIDE
Mesonnoun
(Physics) An elementary particle made up of two quarks; a hadron having a baryon number of zero; any hadron other than a baryon. Mesons are bosons with integral values of spin, having a mass intermediate between those of the electron and a nucleon; they may have positive or negative charges, or may be neutral. Mesons are of three types: the pion (
Wikipedia
Meson
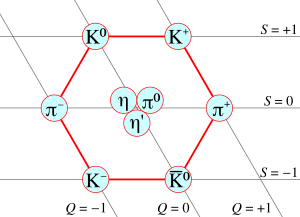
In particle physics, mesons ( or ) are hadronic subatomic particles composed of an equal number of quarks and antiquarks, usually one of each, bound together by strong interactions. Because mesons are composed of quark subparticles, they have a meaningful physical size, a diameter of roughly one femtometre (10−15 m), which is about 0.6 times the size of a proton or neutron. All mesons are unstable, with the longest-lived lasting for only a few hundredths of a microsecond. Heavier mesons decay to lighter mesons and ultimately to stable electrons, neutrinos and photons. Outside the nucleus, mesons appear in nature only as short-lived products of very high-energy collisions between particles made of quarks, such as cosmic rays (high-energy protons and neutrons) and baryonic matter. Mesons are routinely produced artificially in cyclotrons or other accelerators in the collisions of protons, antiprotons, or other particles. Higher-energy (more massive) mesons were created momentarily in the Big Bang, but are not thought to play a role in nature today. However, such heavy mesons are regularly created in particle accelerator experiments, in order to understand the nature of the heavier types of quark that compose the heavier mesons. Mesons are part of the hadron particle family, which are defined simply as particles composed of two or more quarks. The other members of the hadron family are the baryons: subatomic particles composed of odd numbers of valence quarks (at least 3), and some experiments show evidence of exotic mesons, which do not have the conventional valence quark content of two quarks (one quark and one antiquark), but 4 or more. Because quarks have a spin 1/2, the difference in quark number between mesons and baryons results in conventional two-quark mesons being bosons, whereas baryons are fermions. Each type of meson has a corresponding antiparticle (antimeson) in which quarks are replaced by their corresponding antiquarks and vice versa. For example, a positive pion (π+) is made of one up quark and one down antiquark; and its corresponding antiparticle, the negative pion (π−), is made of one up antiquark and one down quark. Because mesons are composed of quarks, they participate in both the weak and strong interactions. Mesons with net electric charge also participate in the electromagnetic interaction. Mesons are classified according to their quark content, total angular momentum, parity and various other properties, such as C-parity and G-parity. Although no meson is stable, those of lower mass are nonetheless more stable than the more massive, and hence are easier to observe and study in particle accelerators or in cosmic ray experiments. The lightest group of mesons is less massive than the lightest group of baryons, meaning that they are more easily produced in experiments, and thus exhibit certain higher-energy phenomena more readily than do baryons. But mesons can be quite massive: for example, the J/Psi meson (J/ψ) containing the charm quark, first seen 1974, is about three times as massive as a proton, and the upsilon meson (ϒ) containing the bottom quark, first seen in 1977, is about ten times as massive.
ChatGPT
meson
A meson is a type of subatomic particle that is composed of a quark and an antiquark. It has zero or integer spin and is subject to the strong interaction or nuclear force. Mesons are intermediate mass particles, heavier than electrons but lighter than protons and neutrons. They often act as exchange particles for the strong nuclear force that holds protons and neutrons together within atomic nuclei.
Webster Dictionary
Mesonnoun
the mesial plane dividing the body of an animal into similar right and left halves. The line in which it meets the dorsal surface has been called the dorsimeson, and the corresponding ventral edge the ventrimeson
Etymology: [NL., fr. Gr. me`son middle, neut. of me`sos, a., middle.]
Wikidata
Meson
In particle physics, mesons are hadronic subatomic particles composed of one quark and one antiquark, bound together by the strong interaction. Because mesons are composed of sub-particles, they have a physical size, with a radius roughly one femtometre, which is about ²⁄3 the size of a proton or neutron. All mesons are unstable, with the longest-lived lasting for only a few hundredths of a microsecond. Charged mesons decay to form electrons and neutrinos. Uncharged mesons may decay to photons. Mesons are not produced by radioactive decay, but appear in nature only as short-lived products of very high-energy interactions in matter, between particles made of quarks. In cosmic ray interactions, for example, such particles are ordinary protons and neutrons. Mesons are also frequently produced artificially in high-energy particle accelerators that collide protons, anti-protons, or other particles. In nature, the importance of lighter mesons is that they are the associated quantum-field particles that transmit the nuclear force, in the same way that photons are the particles that transmit the electromagnetic force. The higher energy mesons were created momentarily in the Big Bang but are not thought to play a role in nature today. However, such particles are regularly created in experiments, in order to understand the nature of the heavier types of quark which compose the heavier mesons.¹
Dictionary of Nautical Terms
meson
A very old form of spelling mizen.
Entomology
Meson
the middle plane of the body.
Usage in printed sourcesFrom:
- [["1707","1"],["1721","14"],["1728","1"],["1734","1"],["1741","1"],["1746","1"],["1750","1"],["1762","1"],["1767","1"],["1776","115"],["1779","4"],["1780","23"],["1782","3"],["1786","2"],["1794","2"],["1795","1"],["1798","6"],["1800","1"],["1803","1"],["1804","2"],["1805","1"],["1807","1"],["1810","2"],["1811","3"],["1812","2"],["1813","1"],["1814","1"],["1815","1"],["1817","3"],["1818","1"],["1819","5"],["1820","4"],["1822","6"],["1823","3"],["1824","14"],["1825","188"],["1826","10"],["1827","9"],["1828","5"],["1829","160"],["1830","47"],["1831","4"],["1832","4"],["1833","2"],["1834","29"],["1835","6"],["1836","33"],["1837","13"],["1838","1"],["1839","4"],["1840","9"],["1841","6"],["1842","3"],["1843","11"],["1844","88"],["1845","27"],["1846","98"],["1847","66"],["1848","22"],["1849","48"],["1850","84"],["1851","76"],["1852","29"],["1853","101"],["1854","30"],["1855","30"],["1856","23"],["1857","8"],["1858","85"],["1859","40"],["1860","27"],["1861","86"],["1862","34"],["1863","7"],["1864","9"],["1865","22"],["1866","23"],["1867","1"],["1868","29"],["1869","28"],["1870","46"],["1871","270"],["1872","18"],["1873","10"],["1874","32"],["1875","22"],["1876","20"],["1877","16"],["1878","4"],["1879","11"],["1880","8"],["1881","34"],["1882","739"],["1883","24"],["1884","71"],["1885","3"],["1886","169"],["1887","32"],["1888","51"],["1889","18"],["1890","15"],["1891","8"],["1892","28"],["1893","67"],["1894","20"],["1895","316"],["1896","24"],["1897","9"],["1898","23"],["1899","50"],["1900","61"],["1901","31"],["1902","62"],["1903","66"],["1904","74"],["1905","117"],["1906","32"],["1907","83"],["1908","127"],["1909","31"],["1910","48"],["1911","96"],["1912","332"],["1913","107"],["1914","146"],["1915","442"],["1916","500"],["1917","99"],["1918","32"],["1919","381"],["1920","35"],["1921","119"],["1922","131"],["1923","525"],["1924","25"],["1925","41"],["1926","121"],["1927","35"],["1928","144"],["1929","34"],["1930","88"],["1931","67"],["1932","37"],["1933","18"],["1934","84"],["1935","111"],["1936","40"],["1937","197"],["1938","175"],["1939","370"],["1940","286"],["1941","176"],["1942","318"],["1943","122"],["1944","112"],["1945","174"],["1946","657"],["1947","607"],["1948","2298"],["1949","1989"],["1950","4005"],["1951","1594"],["1952","9862"],["1953","2480"],["1954","4878"],["1955","8332"],["1956","5099"],["1957","3368"],["1958","6434"],["1959","4961"],["1960","4399"],["1961","4816"],["1962","4241"],["1963","5025"],["1964","3930"],["1965","5074"],["1966","4799"],["1967","3682"],["1968","3302"],["1969","2553"],["1970","2966"],["1971","3521"],["1972","2931"],["1973","3228"],["1974","4645"],["1975","2791"],["1976","1888"],["1977","2686"],["1978","3299"],["1979","3551"],["1980","2412"],["1981","3661"],["1982","2539"],["1983","2416"],["1984","3854"],["1985","4639"],["1986","5154"],["1987","5095"],["1988","5944"],["1989","5169"],["1990","4536"],["1991","3616"],["1992","4353"],["1993","3255"],["1994","3690"],["1995","4671"],["1996","4568"],["1997","3373"],["1998","4211"],["1999","3917"],["2000","5078"],["2001","4541"],["2002","3848"],["2003","5353"],["2004","6257"],["2005","2889"],["2006","3680"],["2007","5237"],["2008","3373"]]
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of MESON in Chaldean Numerology is: 6
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of MESON in Pythagorean Numerology is: 3
Popularity rank by frequency of use
References
Translations for MESON
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
- mesóCatalan, Valencian
- MesonGerman
- mesónSpanish
- mésonFrench
- મધ્યાણુGujarati
- मध्याणुHindi
- մեզոնArmenian
- mesoneItalian
- 中間子Japanese
- មជ្ឈាណូKhmer
- mezonasLithuanian
- मध्याणुMarathi
- mesonNorwegian
- मध्याणुNepali
- mesonDutch
- mesonNorwegian Nynorsk
- mezonPolish
- mésonPortuguese
- мезонRussian
- मध्याणुSanskrit
- mèzōn, мѐзо̄нSerbo-Croatian
- mezónSlovene
- mesonSwedish
- இடையிTamil
- mezonTurkish
Get even more translations for MESON »
Translation
Find a translation for the MESON definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"MESON." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2024. Web. 27 Dec. 2024. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/MESON>.


Discuss these MESON definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In