What does Binocular vision mean?
Definitions for Binocular vision
binoc·u·lar vi·sion
This dictionary definitions page includes all the possible meanings, example usage and translations of the word Binocular vision.
Princeton's WordNet
binocular visionnoun
vision involving the use of both eyes
Wikipedia
Binocular vision
In biology, binocular vision is a type of vision in which an animal has two eyes capable of facing the same direction to perceive a single three-dimensional image of its surroundings. Neurological researcher Manfred Fahle has stated six specific advantages of having two eyes rather than just one: It gives a creature a "spare eye" in case one is damaged. It gives a wider field of view. For example, humans have a maximum horizontal field of view of approximately 190 degrees with two eyes, approximately 120 degrees of which makes up the binocular field of view (seen by both eyes) flanked by two uniocular fields (seen by only one eye) of approximately 40 degrees. It can give stereopsis in which binocular disparity (or parallax) provided by the two eyes' different positions on the head gives precise depth perception. This also allows a creature to break the camouflage of another creature. It allows the angles of the eyes' lines of sight, relative to each other (vergence), and those lines relative to a particular object (gaze angle) to be determined from the images in the two eyes. These properties are necessary for the third advantage. It allows a creature to see more of, or all of, an object behind an obstacle. This advantage was pointed out by Leonardo da Vinci, who noted that a vertical column closer to the eyes than an object at which a creature is looking might block some of the object from the left eye but that part of the object might be visible to the right eye. It gives binocular summation in which the ability to detect faint objects is enhanced.Other phenomena of binocular vision include utrocular discrimination (the ability to tell which of two eyes has been stimulated by light), eye dominance (the habit of using one eye when aiming something, even if both eyes are open), allelotropia (the averaging of the visual direction of objects viewed by each eye when both eyes are open), binocular fusion or singleness of vision (seeing one object with both eyes despite each eye's having its own image of the object), and binocular rivalry (seeing one eye's image alternating randomly with the other when each eye views images that are so different they cannot be fused).Binocular vision helps with performance skills such as catching, grasping, and locomotion. It also allows humans to walk over and around obstacles at greater speed and with more assurance. Optometrists and/or orthoptists are eyecare professionals who fix binocular vision problems.
ChatGPT
binocular vision
Binocular vision is the ability to maintain visual focus on an object with both eyes, creating a single visual image. This vision process allows for depth perception, peripheral vision, and accurate interpretation of the three-dimensional environment. Essentially, it is the coordinated use of two eyes, which produces a sense of depth and gives a three-dimensional quality to the visual experience. It is a trait common to many higher animals, including humans.
Wikidata
Binocular vision
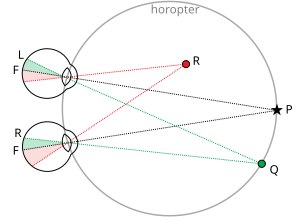
Binocular vision is vision in which both eyes are used together. The word binocular comes from two Latin roots, bini for double, and oculus for eye. Having two eyes confers at least four advantages over having one. First, it gives a creature a spare eye in case one is damaged. Second, it gives a wider field of view. For example, humans have a maximum horizontal field of view of approximately 190 degrees with two eyes, approximately 120 degrees of which makes up the binocular field of view flanked by two uniocular fields of approximately 40 degrees. Third, it gives binocular summation in which the ability to detect faint objects is enhanced. Fourth, it can give stereopsis in which binocular disparity provided by the two eyes' different positions on the head give precise depth perception. Such binocular vision is usually accompanied by singleness of vision or binocular fusion, in which a single image is seen despite each eye having its own image of any object. Other phenomena of binocular vision include utrocular discrimination, eye dominance, allelotropia, and binocular rivalry. Stereopsis is the impression of depth that is perceived when a scene is viewed with both eyes by someone with normal binocular vision. Binocular viewing of a scene creates two slightly different images of the scene in the two eyes due to the eyes' different positions on the head. These differences, referred to as binocular disparity, provide information that the brain can use to calculate depth in the visual scene, providing a major means of depth perception. The term stereopsis is often used as shorthand for 'binocular vision', 'binocular depth perception' or 'stereoscopic depth perception', though strictly speaking, the impression of depth associated with stereopsis can also be obtained under other conditions, such as when an observer views a scene with only one eye while moving. Observer motion creates differences in the single retinal image over time similar to binocular disparity; this is referred to as motion parallax. Importantly, stereopsis is not usually present when viewing a scene with one eye, when viewing a picture of a scene with both eyes, or when someone with abnormal binocular vision views a scene with both eyes. This is despite the fact that in all these three cases humans can still perceive depth relations.
Matched Categories
Numerology
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of Binocular vision in Chaldean Numerology is: 8
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of Binocular vision in Pythagorean Numerology is: 3
Translations for Binocular vision
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
Get even more translations for Binocular vision »
Translation
Find a translation for the Binocular vision definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- - Select -
- 简体中文 (Chinese - Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese - Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Style:MLAChicagoAPA
"Binocular vision." Definitions.net. STANDS4 LLC, 2025. Web. 5 Jan. 2025. <https://www.definitions.net/definition/Binocular+vision>.


Discuss these Binocular vision definitions with the community:
Report Comment
We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.
If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly.
Attachment
You need to be logged in to favorite.
Log In